THE EUROPEAN APP ECONOMY
 PREVIOUS CHAPTER PREVIOUS CHAPTER |
BACK TO CONTENT | NEXT CHAPTER.png) |
THE EUROPEAN APP ECONOMY
Source: VisionMobile.
VisionMobile is the leading research company on theapps economy and mobile business models. Our research
helps clients track app developer trends and master
mobile business models.
INTRODUCTION
A snapshot of the EU app economy in 2014
• 406,000 professional app developers
• 667,000 thousand direct app economy jobs
• 1 million direct and indirect jobs
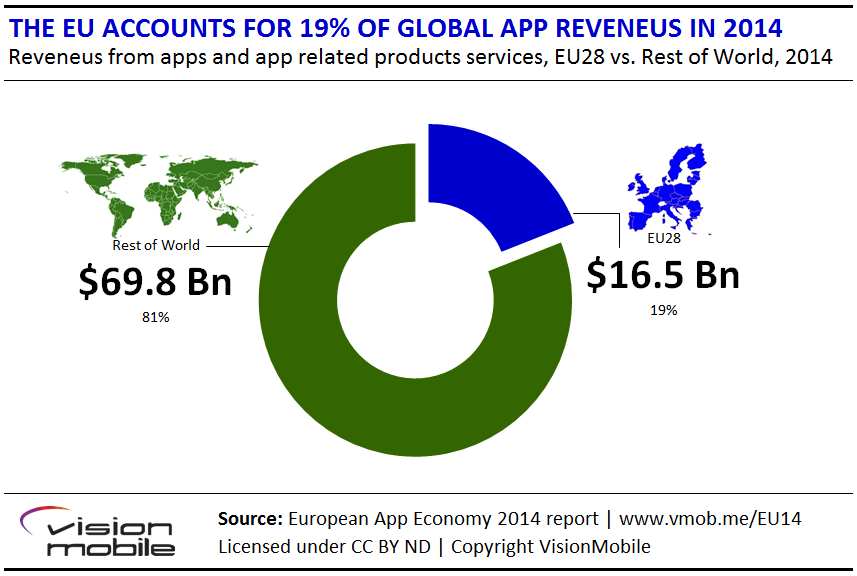
• $16.5 billion in revenues
• 19% of global app economy revenues
• 12% annual growth rate
Business processes are being mobilised
For enterprises, mobilising processes, assets and workforces is becoming a competitive differentiator, driving down costs and increasing productivity.Business demand for apps is already outstripping supply, making developers a hot commodity and app software houses easy acquisition targets.
Mobile is redefining eCommerce
Mobile is redefining commerce and retail. Apps are becoming must-have loyalty and engagement tools for brands. Apps are also the shelf space for services, and goods – both digital and physical, which makes developers the new resellers. Our research shows that eCommerce is the most lucrativerevenue model for app developers, and we expect that its significance willcontinue to grow. In the UK, mCommerce is expected to reach 27% of eCommerce sales in 2014.
Asia is driving growth in the app economy
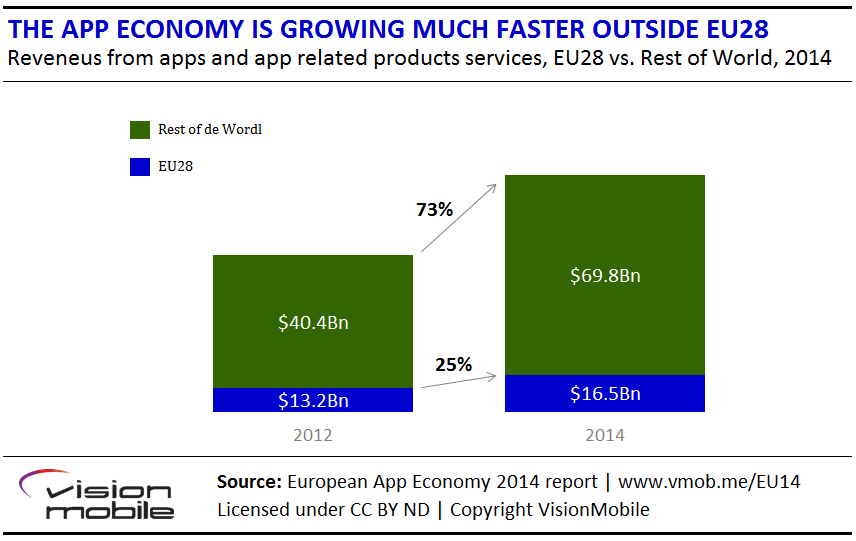
The European Union countries accounted for 25% of the app economy in2012 but dropped to 19% in 2014. China and India will drive smartphone growth in the next few years, while the balance of the app economy isshifting away from Europe and the US.
Apps driving economic growth in the EU
On a regional level, the European Union benefits from the app economy intwo ways. First: directly via jobs and revenues associated with sales of apps and app development services. Second: indirectly via efficiency and productivity gains associated with adoption of mobile apps and services by bothconsumers and industry.
VisionMobile findings are based on our Developer Economics survey series, their 7th edition reaching over 10,000 app developers.
INSIGHT
The European Union has a growing app economy but is losing ground toAsian giants
App development is contributing $16.5 billion to the EU GDP
Smartphone apps and mobile services are continuing to penetrate markets and industries. The app economy is growing at an annual rate of 27% globally, according to VisionMobile’s App Economy Forecasts 2013 - 2016 report, with global revenues from apps and app related products and services forecast at $886 billion for 2014.
Europe is a key player in the global app economy, but its share of global app production has shrunk to 19% of global app revenues, down from 24% of global app revenues in 2012.
EU app economy growing much slower than Asia
App production in the European Union is still growing, albeit at a slower rate than the global app economy. We estimate that app production in the European Union will reach $816.5 billion in 2014, compared to $813 billion in 2012, equivalent to a 12% annual growth rate. At 27%, the growth rate of the global app economy is more than double that of the EU.
In the European App Economy 2013 report, VisionMobile forecast that the global app economy will be growing at a faster rate than the EU countries’. This is due to the rising importance of developing markets that are driven by an unprecedented demand for smartphones and apps.
In 2013 Asia accounted for approximately 3 times the smartphone sales volume of Europe, with a large share of sales to new users. In 2014, India and China alone are expected to add over 400 million new smartphone users. This demand is partly fulfilled through local supply of apps and app develop-ment services.
While EU developers are well positioned to capture a large share of Western markets (North America, South America), they should also aim to extend their reach into fast-growing Asian markets such as China and India.
Language and cultural barriers are significantly higher for EU developers aiming to target these markets and therefore local partnerships will be essential to compete successfully.
Number of global app developers growing to 2.9 million in 2014 With the installed base of smart mobile devices approaching 2 billion, developers have rushed to capitalise on both direct access to consumers and direct access to revenues.
Mobile platforms and app stores have dramatically reduced the cost of app development and the user acquisition cost. As a result developers are flocking to the mobile promised-land in droves.
VisionMobile estimates that the number of mobile app developers globally in 2014 is 2.9 million. Still, we believe that demand outstrips supply, with every self-respecting CIO or brand manager commissioning their own apps. At the same time, there has been an explosion in developer tools, from app prototyping to monetisation and support, with over 1,000 SDK (software development kits) and tools available for app developers. To address the demand for app development, many tools allow apps to be developed and published without writing a single line of code.
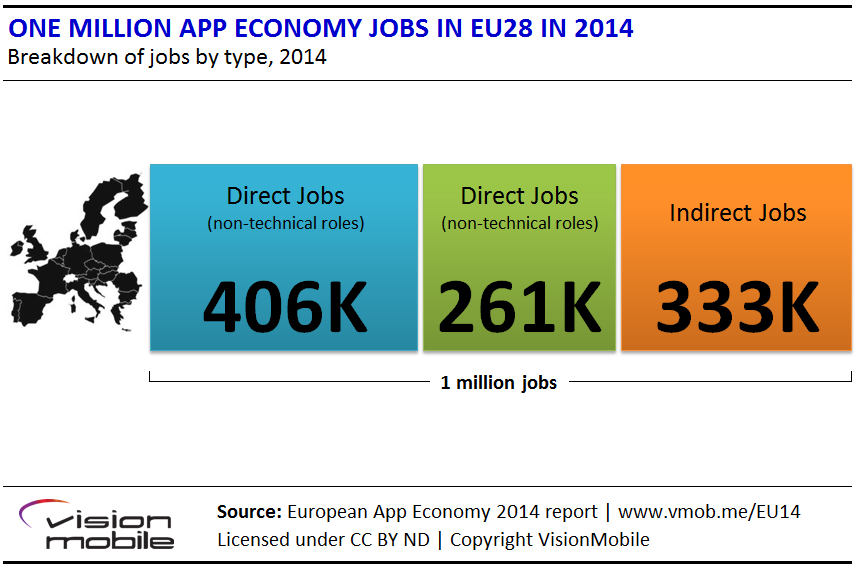
The App Economy contributes 1 million jobs in the European Union
In 2013, VisionMobile estimated that approximately 530,000 jobs in the EU were directly attributed to the app economy. These are jobs that directly support the app business, that is: development, production, marketing and sales of apps or app-related products and services. VisionMobile estimates that the number of direct app economy jobs in the European Union is 670,000 in 2014, representing an increase of 26% compared to 2013. Out of these, 406,000 jobs are developer jobs. The number of people involved in app development is actually higher if Hobbyist and Explorer segments are also accounted for, an additional 255,000 developers (see VisionMobile’s Developer Segmentation report for a definition of segments).
As we noted in the EU App Economy 2013-2016, the app economy has a wider impact on employment, for example creating new jobs in industries that leverage app-related products and services (e.g. health care, automotive, entertainment, education). We had previously used a conservative 1.5 multiplier to arrive at the number of jobs created via spill-over effects of apps into the wider economy. Using the same multiplier we arrive at a minimum of 1 million direct, plus indirect jobs in the EU in 2014, as a result of the app economy.
As the app economy becomes more entrenched in everyday business, spillover effects are increasing and therefore this jobs multiplier should be adjusted accordingly. According to Mandel’s study of the US App* Economy, other studies have used a multiplier between 2.4 and 3.4 in the past, based on the impact of broadband on job creation.
*Mandel, Michael. ”Where the jobs are: The app economy.” South Mountain Economics, LLC. Retrieved June 28 (2012): 2012.
iOS accounts for half the app economy jobs in the European Union
We estimate that at least 497,000 jobs or approximately 50% of all direct and indirect app economy jobs in the EU can be directly attributed to iOS. While Android is used by more developers in the EU compared to iOS; iOS is the preferred platform for professional developers (i.e. excluding Hobbyists and Explorers). It is prioritised by 43% of professional developers vs. 35% for Android. Our research also showed that companies that prioritised iOS also have a higher ratio of non-technical to technical staff.
31% of app developers in the European Union develop commissioned apps
App developers in the EU are more focused on contract development compa-red to developers elsewhere. Almost a third of the EU developer force (31%), generate revenues via contract development, making it the top revenue source for app developers in the EU. In comparison, most developers in other regions (31%) rely on advertising as their primary revenue source.
Contract app development is one of the most lucrative revenue models, whi-le advertising is one of poorest, as we have shown in our Developer Econo-mics Ql 2014 research.
Business and Enterprise apps market to grow to $58 billion by 2016
The popularity of contract development among EU developers is a strong indicator that there is considerable demand from EU verticals entering the app economy and creating a demand for commissioned apps. As smart phone penetration starts to level out in the European Union, businesses will play an increasingly important role in the growth of the app economy in the region.
As VisionMobile highlighted in our Business and Productivity Apps report, this sector will experience a rapid growth and we expect that it will reach 858 billion globally by 2016. The enterprise app sector presents new opportuni-ties and better revenue potential for developers, compared to the consumer sector.
VisionMobile has identified 5 areas where app developers and start-ups can add value in the business & enterprise app sector:
- Vertical market specialisation
- Productivity/BYO apps
- Mobile SaaS
- Bespoke enterprise apps
- Mobile application and device management
.png)
.png)
GNSS and location-based services trends
Source: GSA Market Report 2013
Market segmentation
The GNSS market comprises products (receivers and devices) and services using GNSS-based positioning as a significant enabler. The GSA segments the market according to the following 7 market domains:
- Location-Based Services (LBS), where GNSS is used to enable a vast range of LBS
- Road, whereas GNSS is used for navigation, Road User Charging, Pay-Per-Use-Insurance, and to support the provision of Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) applications (such as eCall and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems)
- Aviation, including GNSS-certified devices for commercial, regional, general & business aviation, and uncertified devices aiding pilots flying under Visual Flight Rules (VFR)
- Rail, in which GNSS is used in safety-critical devices supporting and non-safety devices supporting other applications (e.g. asset management and passenger information)
- Maritime, whereas GNSS is used to support general navigation, the Automatic Identification System, the Long Range Identification and Tracking System, port operations, dredging and search & rescue beacons
- Agriculture, including GNSS devices used for tractor guidance, automatic steering, asset management and Variable Rate Technology (VRT)
- Surveying, where devices are GNSS-enabled to support land surveying (including cadastral, mining, construction, and mapping) and marine surveying (including hydrographic and off-shore surveys)
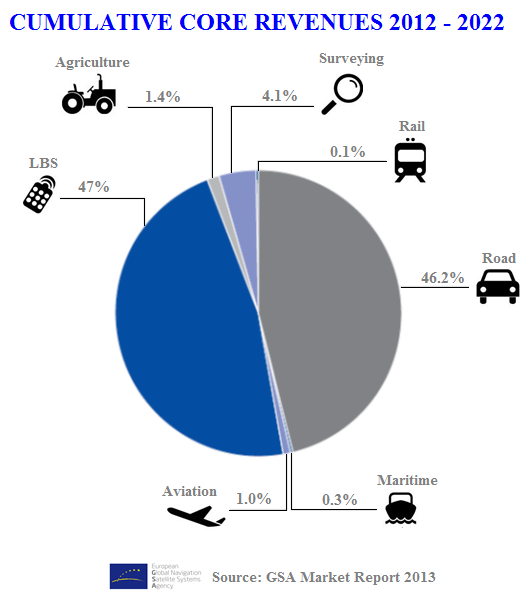
According to the GSA "GNSS Market report Issue 3" 2 the LBS segment leads global GNSS revenues, which are expected to account for the 47% of the worldwide cumulative core revenue for the years 2012-2022. LBS is also forecast to be the largest market segment by revenue, overtaking Road, where the Portable Navigation Device market continues to decline, being cannibalised by the use of smartphones in cars. Moreover, LBS devices are also being increasingly used in general aviation and leisure maritime.
|
http://www.gsa.europa.eu/sites/default/files/GSA%20-Market%20Report%202013%20new.pdf |
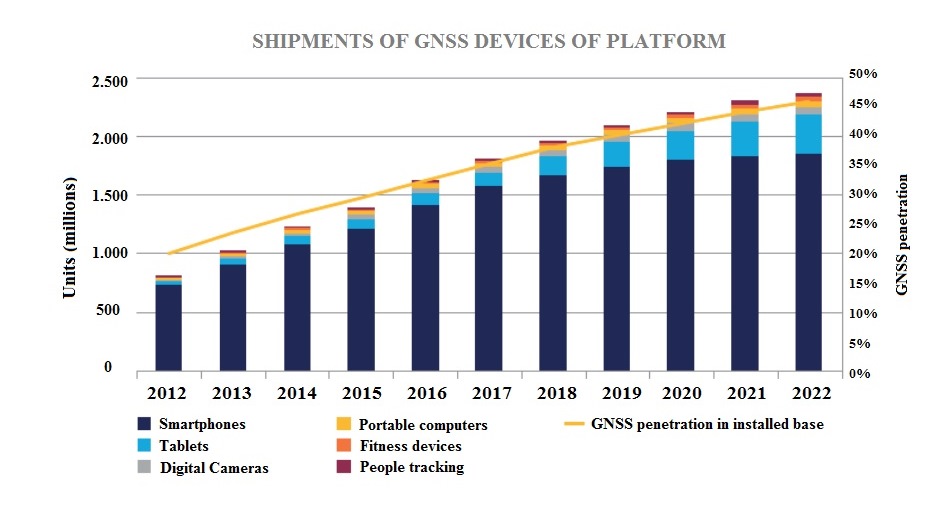
Market development
LBS market has shown a phenomenal in the last years: global shipments of GNSS-enabled LBS devices have grown from 150 million to 800 million between 2007 and 2012 (40% CAGR). In addition, the integration of GNSS and other positioning technologies in devices traditionally unrelated to location, together with the emergence into the market of new devices, has triggered an unprecedented demand for LBS. In fact, on top of smartphones - clearly representing the champion of the LBS market - GNSS capability is now a common feature in an increasing number of portable devices:
- Tablets normally integrates GNSS capabilities to provide location enhanced apps
- More and more portable computers are GNSS-enabled to best take advantage of LBS
- Most of digital cameras available into the market employs GNSS capabilities to geo-tag video clips and photos
- Fitness devices track the distance covered by runners thanks to integrated GNSS receivers
- People Tracking use GNSS to track persons. Moreover, smart watches and other wearable technologies (e.g. Google glasses) recently entered into the market and often integrate built-in GNSS receivers to provide innovative services such as location based information in camera view (augmented reality).
The mass diffusion of such devices together with the fact that they integrate other positioning technologies such as Cell ID, Wi-Fi and INS has led to an upsurge in number of available apps (c. 700,000 apps are now available in Google Play store compared to 88,000 in 2011) and even more applications were available in Apple App Store. Out of these, a significant number make use of location information: GSA estimates that 40% of available applications use location information, normally provided by built-in GNSS receivers. Among successful applications relying on positioning information are:
- Mobility-related ones, such as personal navigation and point of interest search
- Applications contributing emergency services providers and individuals to locate persons or objects, such as emergency caller location and person and objects tracking
- Apps aimed at providing entertainment, e.g. location based gaming, sport and entertainment and social networking
- Location based advertising, integrating mobile advertising with location based services to best target potential customers
- Applications dedicated to provide information according to persons’ location, e.g. weather information and news
Such LBS, commonly used nowadays by millions of persons, represent a per-fect fit with the increasingly fast pace of life, especially in large cities. With an outlook towards the future, clear signs suggest that an even a higher diffusion of LBS is expected to come in the next years. Indeed, re-cent technological trends, such as the emergence of augmented reality and indoor positioning technologies, the improvement in the quality and capacity of data connectivity and the continuous improvements in cost and power consumption of devices suggest that application developers will be able to create new and more powerful Location Based applications. Moreover, positioning performances will strongly benefit of the introduction of new GNSS such as Galileo. As a part of a multi-constellation solution, Galileo can respond to the need for higher accuracy for some more demanding applications. Similarly, availability and Time To First Fix will be further improved by the use of Galileo satellites, enhancing continuity of service in urban environ-ments. In addition, state-of-the-art signal characteristics of Galileo will have better resistance to multipath interference (interference from reflected sig-nals). In light of the fact that GNSS remains the primary positioning solution outdoors, offering better accuracy than Cell ID and Wi-Fi, app developers will be empowered with the possibility of enhancing the functioning of already established apps or the creation of new ones. Finally, the proliferation of different typologies of GNSS-enabled devices combined with a drop in the price of the devices will further boost the global shipments of GNSS-based devices. Consequently, an increasing number of consumers in developed countries will make use of more than just one device while more and more persons will be able to afford the purchase of a GNSS enabled smartphone in developing countries.
From a geographic perspective, the EU LBS market will continue to grow, both in terms of shipments and revenues:
• EU27 installed base is expected to top 1.28 billion of units in 2022 (13% CAGR over 2012)
• EU27 core revenues are estimated to be in the order of 11.6 €billion in 2022 (19% CAGR over 2012)
It indicates that even in developed countries the market remains far from saturated and, according to GSA, it makes EU27 the second fastest growing LBS market in terms of revenue in the world, behind the “rest of the world” (CAGR 23%) and before “North America” (CAGR 15%).

 PREVIOUS CHAPTER PREVIOUS CHAPTER |
BACK TO CONTENT | NEXT CHAPTER.png) |